You are here
Moscow Public Library
The Mission Revival Moscow Public Library is a testament to the passion and drive of two women’s groups who mobilized the community and secured Carnegie funding for library construction. While the initial Carnegie building symbolizes aspirations for education, culture, self-improvement, and community-building in the Progressive Era, the 1983 addition is the result of a decade of discussion and deliberation that affirmed the perseverance of library supporters and the established community’s commitment to honor its past while accommodating a growing and changing constituency.
This story began in 1885 with the establishment of a Women’s Reading Room Society in downtown Moscow. By 1904, members of two women’s groups, the Pleiades Club and the Ladies Historical Club, formed a library committee and began planning and raising funds for a new building. The committee’s secretary, Mary Forney, requested and received $10,000 in Carnegie Library Endowment Funds for library construction once the community procured a site and the city agreed to provide annual operating expenses. In 1905 Moscow citizens voted in favor of a permanent tax to support the library. A mayor-appointed library board and the two clubs raised funding to purchase a corner site two blocks from Main Street at the edge of the residential Fort Russell neighborhood.
In 1905 the board hired Boise architect Watson Vernon to design the library in the Mission Revival style, unusual for a library—especially in northern Idaho. Boise contractor Fred King Company began construction in the summer of 1905 and completed the building in the spring of 1906. Although the board planned to move into the new library at the beginning of April 1906, plans changed when the University of Idaho’s Administration Building burned to the ground on March 30th of that year. To accommodate the university, the library was used as classroom space until the end of the 1906–1907 academic year. University classes took place in the library until midafternoon each day, when the building opened for regular library use.
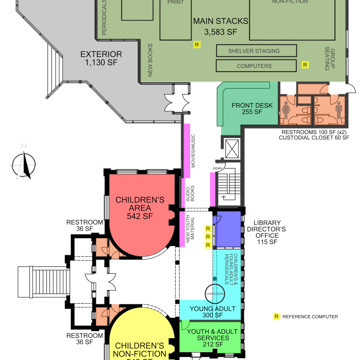
The library sits on a sloped site that enhances the drama of procession to the elevated entrance as seen by pedestrians walking uphill from downtown. The original Mission Revival building is symmetrical and rectangular in plan, with a rusticated sandstone raised basement supporting buff brick walls accented with sandstone lintels, stringcourse sills, and coping above. True to the Mission Revival style, the library has defined corner piers and decorative curvilinear parapets extending above a terra-cotta tile roof. The front of the central porch, to which visitors ascended by a pair of curved stone staircases, has its own decorative curvilinear parapet, perforated by a large semicircular arch. Inside, a circular librarian’s desk originally dominated the central space, which was a flanked by two reading rooms flooded by daylight through large rectangular windows capped with fanlights. The semi-cylindrical shape of the reading rooms eliminates hidden corners and allowed panoptical surveillance by a single librarian.
Over time, the building expanded to accommodate its growing and changing constituency. In 1931, the library board hired contractor Roy Moerder to prepare plans to double the stack and office space by removing the library’s back wall and extending the building to the east. Following Moerder’s plans and specifications, John Eisinger completed the addition by October 1931, extending the original north and south walls with buff bricks salvaged from the demolished east wall. In building the new east elevation, invisible from the street, Eisinger did not attempt to match the original building; instead he built it of red brick walls and rectangular windows. Other changes were the result of maintenance issues: in 1938 the deteriorating curved stairs of the entrance were replaced with a single, straight staircase.
The 1960s and 1970s were decades of change and activism for the library and its community. This began in relatively minor way with the 1964 remodeling of the basement from a clubroom into a children’s library. More significantly, in 1967, the Moscow Public Library merged with the Latah County Library to form the Moscow–Latah County Library District. The county library moved its collection into the Moscow Library, making it the headquarters for the entire district. By 1971 a citizens’ panel studied the library’s needs and urged administrative bodies to seek funding for a new facility. In 1972, the library board purchased two lots to the north of the library for $35,000. The following year the board hired a local firm, Architectural Workshop, to complete a building program and feasibility study that considered alternatives such as demolishing the existing building and rebuilding from the ground up, adding onto the original building, building on a site in a different location, or adapting the old post office for use as a library.
Next, the board then hired Coeur d’Alene architect R. G. Nelson to design a new 16,000-square-foot building. In 1977, Nelson presented a schematic design for a new building that some community members felt was inappropriately modern for a historic residential neighborhood. Public discussion of the feasibility study and schematic design drew many community members into a conversation about inadequate space, poor repair, and inaccessibility of the historic building. The conversation expanded to consider the library within the context of Moscow’s historic core. A citizen’s group, the Fort Russell Neighborhood Planning Association, advocated preserving the Carnegie library and requiring that any new building be “in harmony with the scale and character of the area.” Public appreciation of the historic Carnegie library led to its nomination to the National Register of Historic Places in 1978.
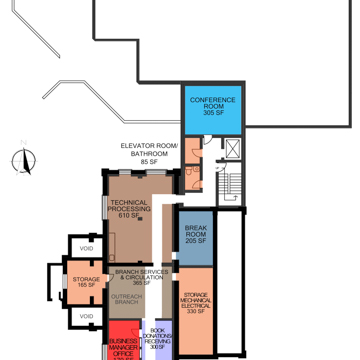
In 1977 and 1978 the board presented bond levy elections to voters of the Moscow and Latah County Library District to raise money for a new library building. Although the elections passed in Moscow, they failed in the county. By 1982, the library had hired another architecture firm, Hummel, Jones, Miller and Hunsucker. Project Architect Nelson Miller designed an addition that, while modern, was sympathetic to the historic building. His design was disseminated to the public in 1982, as the library board presented another bond levy to Moscow voters for $485,000 to renovate and add onto the existing library building; the bond passed. The Latah County District contributed savings, donations, and some annual funding for furnishings. Miller completed construction bid documents by July and the library board hired Great Northern Construction Company from Coeur d’Alene. Great Northern broke ground in August 1982 and the expanded library opened to the public in April 1983.
The 1983 addition preserves and complements the original building in both material and form. Buff brick walls of the addition match the original. A semicircular arch through the north wall echoes the semicircular arch of the original building’s entrance porch. Most importantly, the new library building steps back, literally, allowing the older building to take center stage. The newer building asserts its modern identity with large panes of south-facing glass that contrast in form with the round-arched windows of the original, yet they achieve the same end—to flood the reading area with daylight.
The library continues to serve as an active cultural and social node in the Moscow community. In 2013 City Council provided $25,000 to add to the $50,000 raised by the Library Friends to upgrade the library entrance. Jacob Osborne of Cobblestone Landscaping designed a new ADA-compliant entrance ramp and a pedestrian plaza to accommodate a variety of library programs. Completed in 2014, the new landscape design includes new seating, LED lighting, and water-wise and pollinator friendly landscaping.
References
Hibbard, Don, “Moscow Carnegie Library,” Lath County, Idaho. National Register of Historic Places Inventory-Nomination Form, 1979. National Park Service, U.S. Department of the Interior, Washington, DC.
Neil, J. Meredith. Saints and Oddfellows: A Bicentennial Sampler of Idaho Architecture. Boise, ID: Boise Gallery of Art Association, 1976.
Monroe, Julie R. Moscow: Living and Learning on the Palouse. Charleston, SC: Arcadia, 2003.
Moscow Library Collection (meeting minutes, correspondence, newspaper articles, and other papers and images related to design and construction of the Moscow Library). Latah County Historical Society, Moscow, ID.
Moscow-Latah County Library System Board. Board Reports 1965–1983. Moscow Public Library, Moscow, ID.
Otness, Lillian Woodworth. A Great Good Country: A Guide to Historical Moscow and Latah County, Idaho. Moscow, ID: Latah County Historical Society, 1983.
Spurling, Carol. Moscow Public Library: A Century of Service 1906-2006. Moscow, ID: Moscow Public Library, 2006.
Writing Credits
If SAH Archipedia has been useful to you, please consider supporting it.
SAH Archipedia tells the story of the United States through its buildings, landscapes, and cities. This freely available resource empowers the public with authoritative knowledge that deepens their understanding and appreciation of the built environment. But the Society of Architectural Historians, which created SAH Archipedia with University of Virginia Press, needs your support to maintain the high-caliber research, writing, photography, cartography, editing, design, and programming that make SAH Archipedia a trusted online resource available to all who value the history of place, heritage tourism, and learning.